Laser Hardening Services
Laser hardening is a cutting-edge surface treatment process used to increase the hardness of specific areas on metal parts. It utilizes focused laser beams to rapidly heat a material’s surface, followed by immediate cooling. This rapid process results in a hard, durable surface while preserving the underlying material’s properties, making laser hardening ideal for high-performance applications.
What Is Laser Hardening?
Laser hardening involves high-powered lasers to heat the surface of a metal part to a temperature above the transformation temperature of the material, followed by a rapid self quenching process of the material. This causes the material’s surface to harden while the core remains unaffected. The method offers precision and control, enabling manufacturers to selectively treat specific areas of a part that require enhanced wear resistance.
How Does Laser Hardening Work?
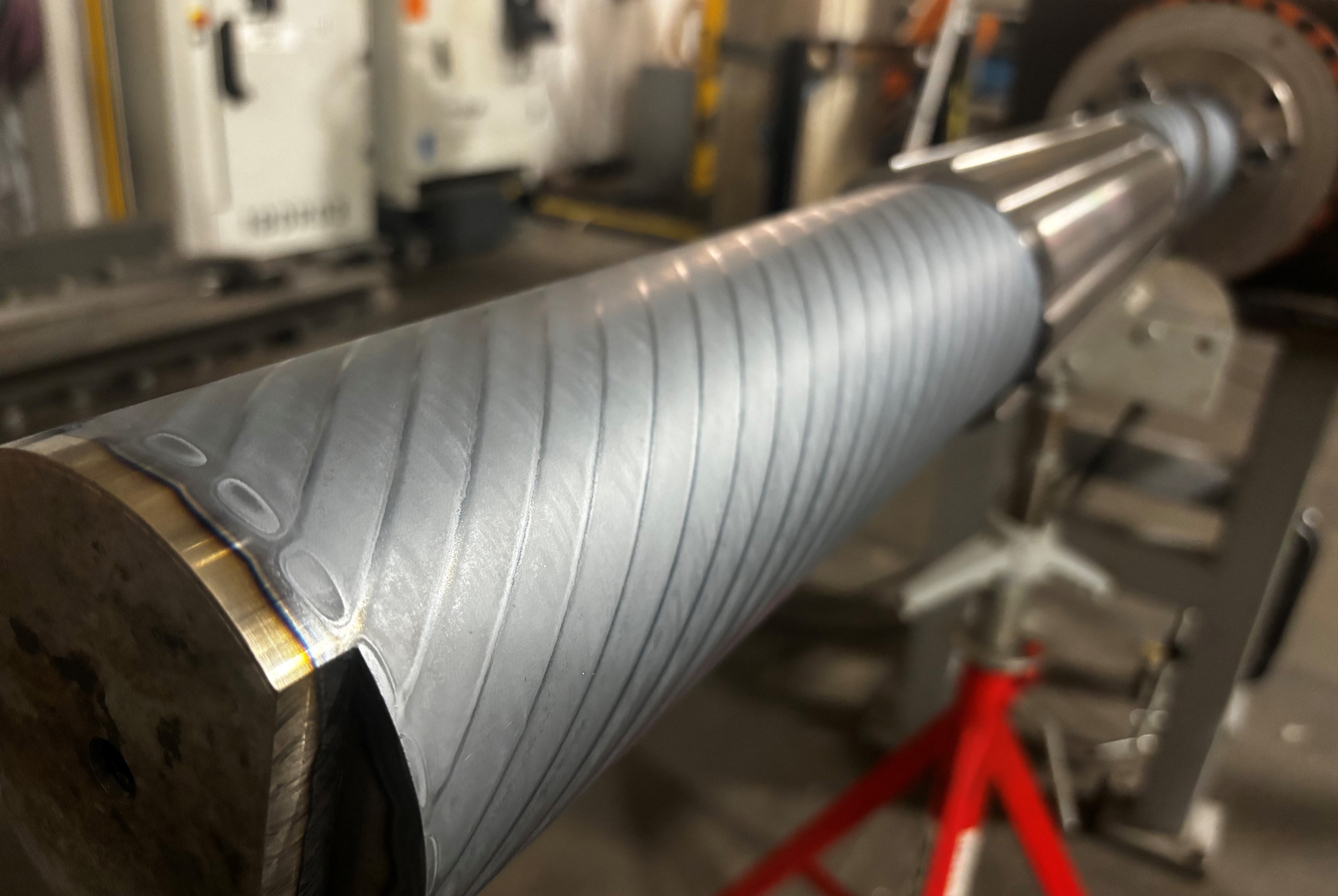
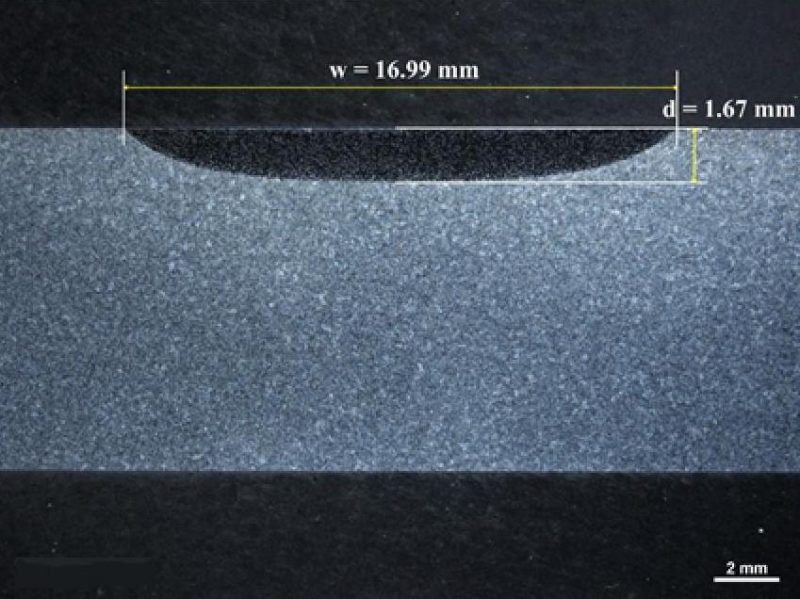
Laser hardening operates by focusing a high-powered laser beam onto the surface of a metal part. The laser quickly raises the temperature of the surface to a level where it begins to harden, typically above transformation temperature of the material. Rest of the metal self quenches the heat. The result is a hardened surface with improved wear resistance, while the underlying material remains unaffected and retains its original mechanical properties. While traditional hardening methods like flame, induction, and oven-based techniques have been used for decades, they often come with a downside—significant distortion. This requires additional steps, like hard milling, straightening and in materials like AISI D2, double tempering, to mitigate cracking risks. However, these extra steps add time and cost to the process. Laser Hardening process results in minimal to zero distortion there by avoiding a need for additional processing steps such as hard milling or straightening. Typical hardness case depths range from 0.040″ to 0.080″ (1- 2 mm). Laser Hardening in most cases achieves the maximum hardness the material is capable of achieving.
Any material with 0.2% or higher carbon can be laser hardened. Common materials compatible with Laser Hardening include:
- S0050A Alloyed Steel
- A2 Tool Steel
- D2 Tool Steel
- S7 Tool Steel
- M2 Tool Steel
- 4140 Alloy Steel
- 420 Stainless Steel
- Caldie
- D6510 Ductile Iron
- S7140 Alloyed Steel
- G2500 Grey Cast Iron
- G25HP Grey Cast Iron
- G3500 Grey Iron
- D4512 Ductile Iron
- S0030 Non-Alloyed Steel
- P20 Steel
Benefits of Laser Hardening
Laser hardening provides several key advantages, including:
- Consistent heat treating depths: The laser’s focused energy allows for precise treatment of specific areas, ensuring minimal distortion and maximum efficiency.
- Minimal to no distortion: Unlike traditional heat treatment methods, laser hardening produces minimal heat-affected zones, reducing the need for post-processing.
- In-process quality control: The hardened surface improves wear resistance, extending the service life of components subjected to high stress and wear.
- Cost Efficiency: The process is highly efficient, with minimal energy required compared to conventional heat treatments, making it both cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
- Consistent Hardening: With the use of advanced feedback-controlled process and proprietary process control algorithms, Synergy can provide extremely consistent hardness (within +/- 1 HRC) and hardening depths
What Laser Hardening Services Do We Offer?
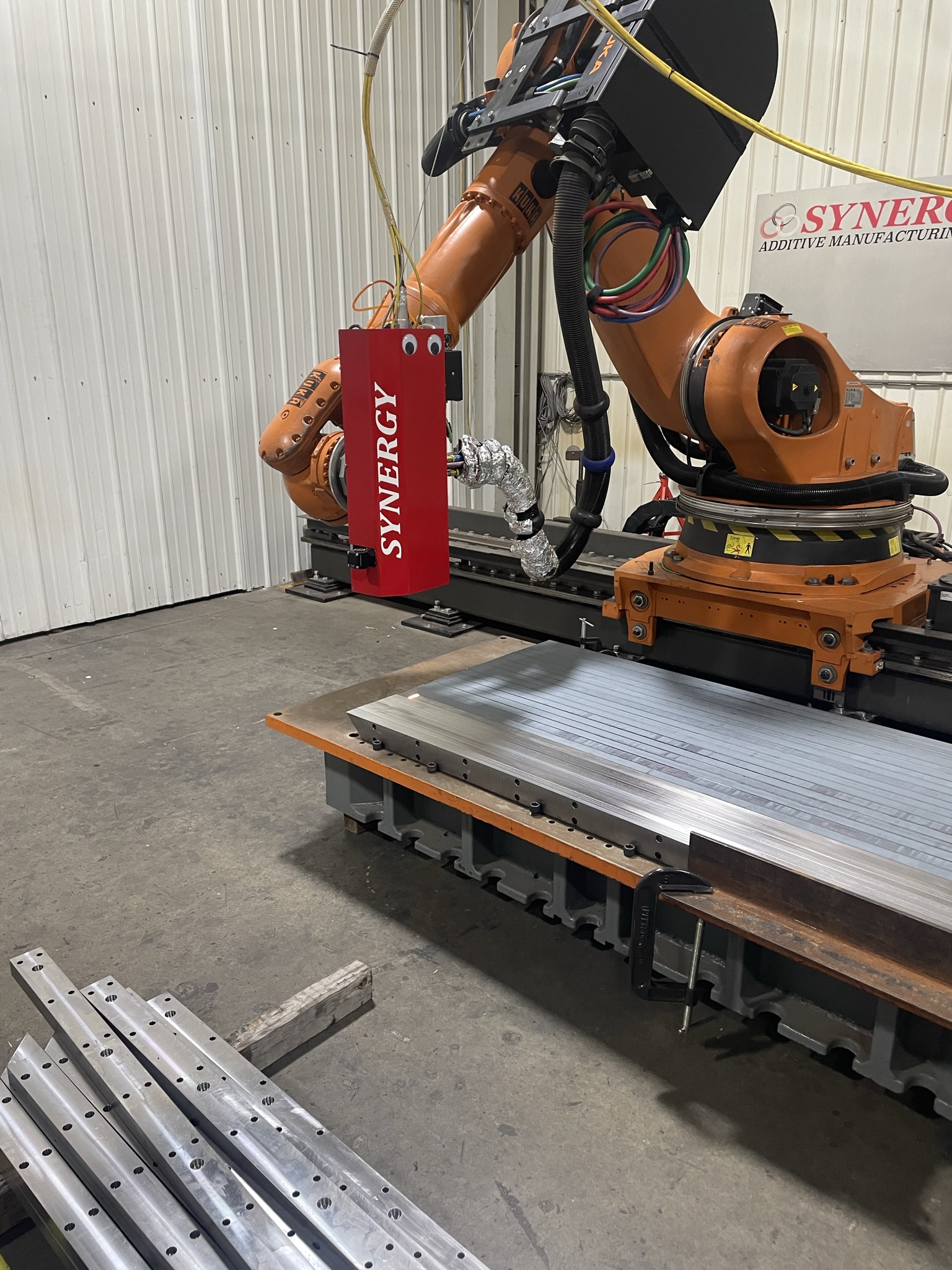
Laser heat treatment of your tools, dies, or other applications creates a lasting impact with precise control of heat input, minimized stress and distortion, repeatability, time efficiencies, and line-of-sight access for harder to reach areas.
At Synergy Additive, we offer comprehensive laser hardening services tailored to your specific needs. Our services include:
- Tool & Die Hardening: We specialize in hardening tooling materials, improving the longevity and performance of dies and molds used in manufacturing processes. Most common Cast Iron materials such as D6510 and tool steels such as S7140, 4140, D2 etc. are good cases for laser hardening.
- Shaft Hardening: Hardening shafts using lasers eliminate the need for post grinding operations. On materials such as 4140, 4340 Laser Hardening results in hardness in the range of 55-60 HRC.
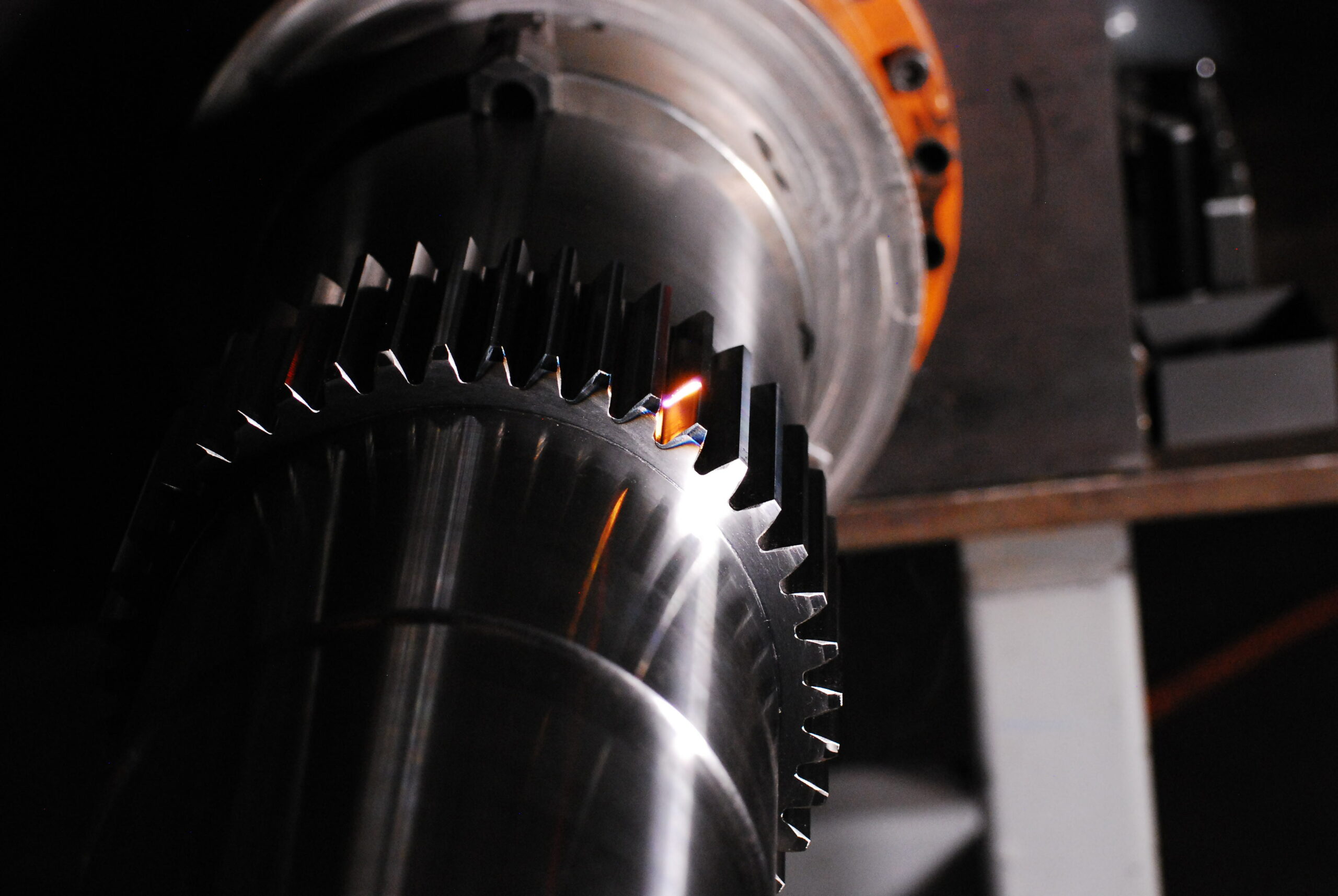
- Gear Hardening: Precision hardening of individual gear tooth faces achieves the desired hardness while preserving material ductility in other areas, thereby reducing the risk of root cracking.

Is Laser Hardening the Same as Induction Hardening?
Laser hardening and induction hardening are both surface heat treatment processes designed to improve the hardness and wear resistance of materials, but they differ in how they apply heat. In laser hardening, a laser beam is focused onto the surface of the material, rapidly heating it to the required temperature before it cools quickly. This results in a hard surface layer. In contrast, induction hardening uses electromagnetic induction to heat the surface of a metal part, followed by quenching to achieve similar hardness.
The key difference lies in the method of energy application—laser hardening uses a focused laser beam, while induction hardening uses induced electrical currents to heat the material. While both methods achieve similar results in terms of surface hardness, laser hardening is often more precise and can target specific areas and produces minimal to zero distortion, while induction hardening is typically used for larger parts or those requiring deeper hardening.
Laser Hardening Vs. Conventional Processes
Laser heat treating is ideal when distortion is a critical factor in the manufacturing process. Laser heat treating results in minimal to no distortion, there by reducing the requirement for post machining or straightening operations.
| Processes | Laser Heat Treating | Induction Heat Treating | Flame Heat Treating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Hardness | Max Hardness | High-Max Hardness | Med-High Hardness |
| Typical Hardness Depth | Up to 0.080″ (1-2 mm) | Up to 0.0120″ (3 mm) | Up to 0.0120″ (3 mm) |
| Hardness consistency | +/- 1 HRC | +/- 2-10 HRC | +/- 2-10 HRC |
| Potential for distortion | Zero – Minimal | Medium – High | High |
| Precision control | Highly precise | Medium – Low precision | Low precision |
| Process automation | Robotic / Feedback controlled | Manual operation | Manual operation |
| Overall Cost Savings | 20%+ | baseline | baseline |
READ MORE ON LASER HARDENING HERE:
- Laser hardening process steps
- Laser Hardening of important material – D2 tool steel
- Laser hardening of trim inserts
- Laser hardening of hot stamping dies
- Benefits of Robotic Laser Hardening and tool path programming
- Laser heat treating case studies – published in Heat Treat today Magazine
- Energy Efficiency and sustainability of Laser Hardening – published in Heat Treat today Magazine
- Article published in Heat Treat Today on advantages and cost savings of Laser Hardening